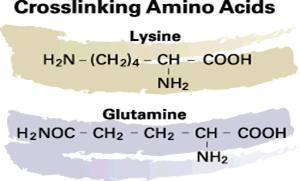
TG crosslinks proteins by forming covalent bonds
between two amino acids, glutamine and lysine.
Transglutaminase(TG)
|
Transglutaminase works effectively in a variety of foods due to its unique properties. It is active over a fairly wide pH and temperature range. |
Firstly,transglutaminase enzyme approved for use in all non-standardized processed meat and poultry products. And after,it approved its use in processed seafood. The enzyme, TG, crosslinks protein molecules in food to form firmer textured meat and seafood products without using binders or salt and for use in meat substitutes as well as refrigerated and frozen yogurt products and also nucleotides synergize with MSG to deliver "umami," the fifth basic taste.
The approved enzyme for use in meats, poultry, seafood and cheese, a unique transglutaminase (TG) enzyme gives food formulators the opportunity to be creative.
For example,when caseinate is mixed with water, it will not gel. However, with it added the transglutaminase crosslinks the protein, causing it to gel without heating. TG also has the potential to join two different proteins that normally are not linked together.It gives one the potential to create designer proteins.
|
|
Produced via microbial fermentation, TG crosslinks proteins by forming covalent bonds between two amino acids, glutamine and lysine. TG is also calcium independent.
Transglutaminase enzymes from different sources such as animal tend to require calcium in order to be active. Being calcium independent makes it easier to use TG in a wide range of products.
In addition to its ability to create new products,TG used for restructuring products, which can often lead to cost savings. In the U.S., Ajinomoto sells TG in preparations for specific end applications.
Another TG formation,consists of the transglutaminase enzyme with caseinate and maltodextrin. It can use this preparation to restructure foods that contain proteins in forms that are unavailable for reaction. With red meat,that allows processors to utilize the trim from steak. Adding TG allows formulators to restructure the trim into a portionable form. TG can also reduce salt levels in processed meats.It works similarly in seafood.
Another type of TG,improves texture in products where there is enough protein available for the reaction to occur, such as an emulsified meat product. The preparation also works in dairy systems.
And another type, which consists of transglutaminase with maltodextrin, starch and sodium phosphate, modifies the texture of seafood like block set surimi, enabling the use of lower grades of surimi while maintaining similar texture.
In yogurt, one of the biggest effects of transglutaminase is that it reduces syneresis. In frozen desserts, it changes the mouthfeel properties, especially in low-calorie or sugar-free products. Grains and cereal-based products such as pasta are potential applications. Ajinomoto is planning to release additional preparations for use in these and other food applications.
The TG for use in modified fat and/or sodium processed meat and poultry products and all non-standardized processed meat and poultry products and all types of processed seafood, natural cheese, processed cheese, cream cheese, yogurt and frozen desserts at various levels in ppm level.